Click on the boxes below to expand them and view an explanation for each term.
The variety of living species on the Earth. This includes plants, animals, and bacteria.
Carbon is an element that all living creatures are made up of. When living creatures die, they are buried under sediment and become a source of carbon storage. But since the 1800’s industrial revolution we have been digging up this carbon to power machines – hence the name fossil fuels.
Your carbon footprint is made up of all the emissions that are caused by you in a given time period (usually a year), either directly, such as driving, or indirectly, such as emissions caused by food you eat.
The action or process of removing an equal amount of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere that has been released.
Carbon dioxide, one of the main greenhouse gases.
CO2e, or carbon dioxide equivalent, is a term used to describe all greenhouse gases as a standard unit. For any type or quantity of greenhouse gas, it represents the amount of CO2 that would cause the same amount of global warming.
An electric vehicle charging point is equipment that connects an electric vehicle (EV) to a source of electricity to recharge electric cars.
The distance between the place where food is grown or made and the place where it is eaten.
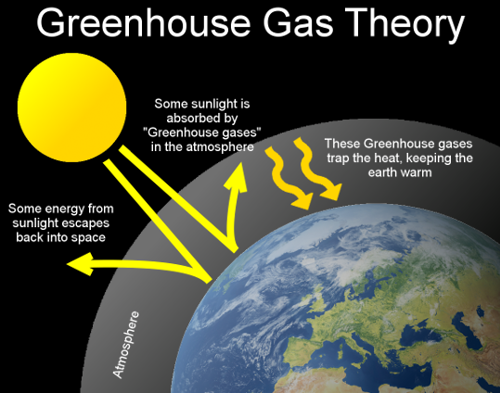
A greenhouse gas is any gas in the atmosphere which absorbs and re-emits heat, keeping the planet’s atmosphere warmer than it would normally be.
The practice of making a misleading claim to make something appear to be more environmentally friendly than it really is.
Photovoltaic or Solar Energy – conversion of light into electricity using semi-conducting materials
The point at which carbon emissions in the atmosphere are balanced with carbon removal from the atmosphere.
Achieving net zero carbon means reducing carbon emissions to almost zero and then safely removing the equivalent amount of remaining emissions from the atmosphere (offsetting), for example by rewilding or planting trees. Net zero carbon is different to 'zero carbon' which requires an activity to produce no carbon.
Watch a video from the National Grid.
Energy that comes from naturally replaced resources, such as sunlight, wind and waves.
The process of protecting an environment and returning it to its natural state, for example by bringing back wild animals that used to live there.
Emissions that come directly from operations that are owned or controlled by us/you – fleet, cars, buildings.
Indirect emissions but in our control, eg. Purchased or consumed electricity, heating or cooling.
Indirect emissions outside our control that occur in the value chain, e.g. community, investments, purchased goods and services.
Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment recycling; a specialist part of the waste and recycling industry.